-
Architects: Bio-architecture Formosana
- Area: 28580 m²
- Year: 2021
-
Photographs:Studio Millspace, Yue-Lun Tsai
-
Lead Architects: Ying Chao Kuo
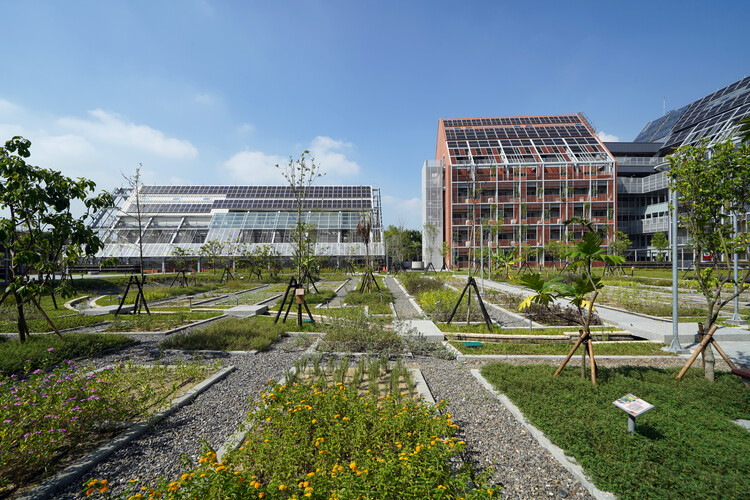

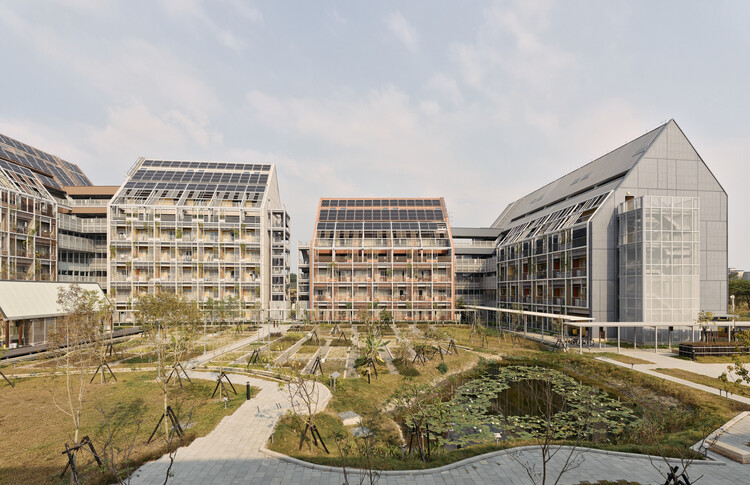
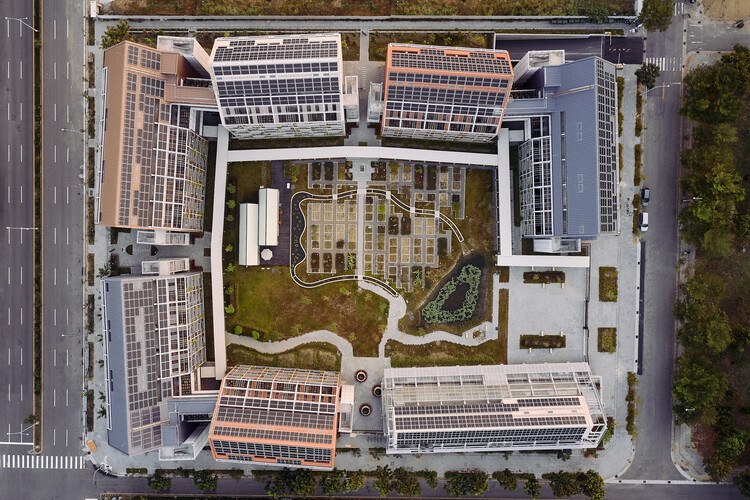
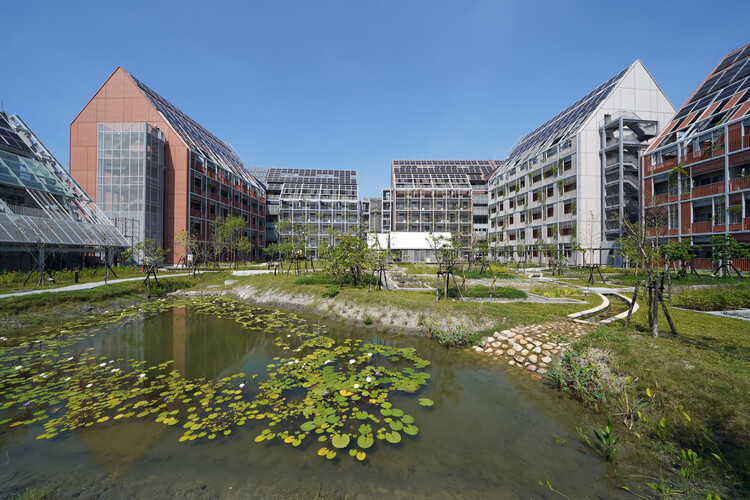
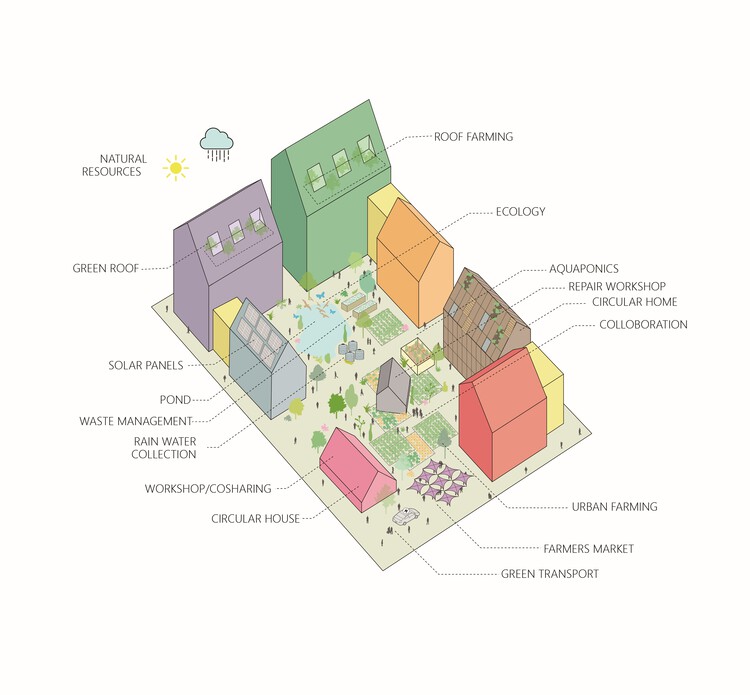
Text description provided by the architects. Modularization is crucial in larger-scale urban developments to make fabrication assembly and disassembly more efficient and simplify the stocks of building material banks. The “Circular Village” is made up of the three “Circular Blocks” where the living quarters are located, “Circular Field” where it consists of a “C-House,” an “E-House” and a “C-Farm.” The C-House functions as the living room of the village, the E-House as the kitchen, while the C-Farm is the garden where food is produced.
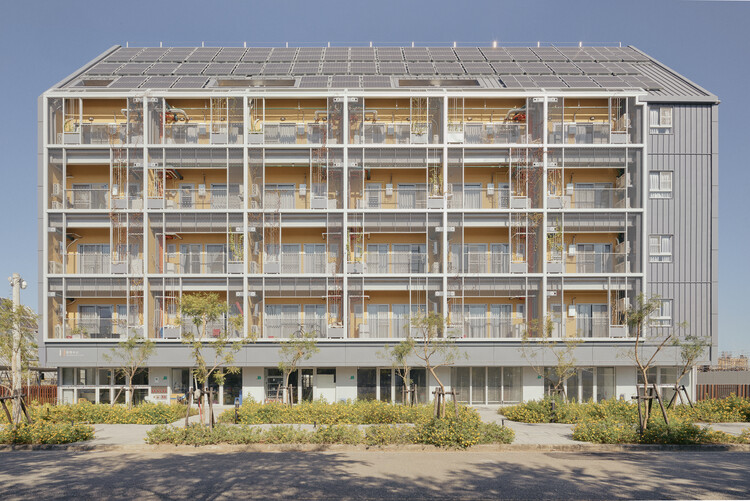


In the circular economy, materials are reused and virtually no waste is created. The design stage takes into account assembly in construction and deconstruction after use. Some of the materials used include recycled and green materials. For instance, the salvaged hardwood from TaiSugar’s old dilapidated buildings was used as the main structure for the E-House while their recycled railway tracks were designed as a fence on the ground periphery.
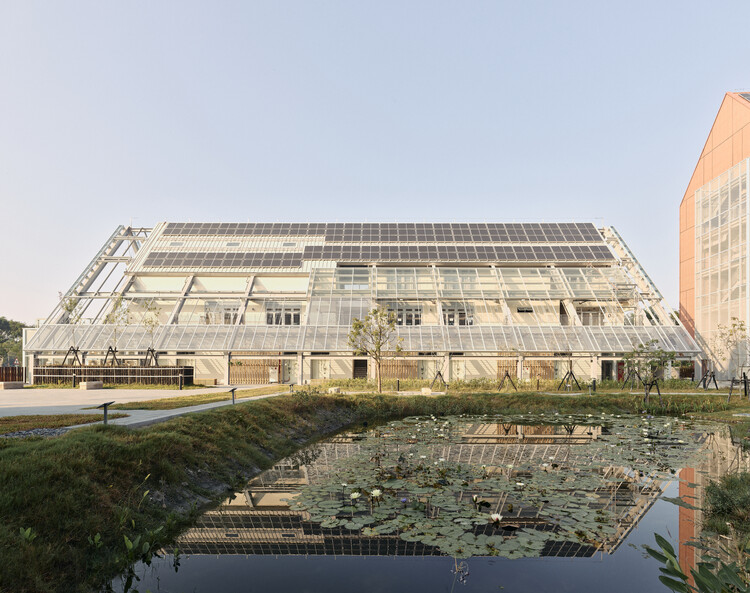
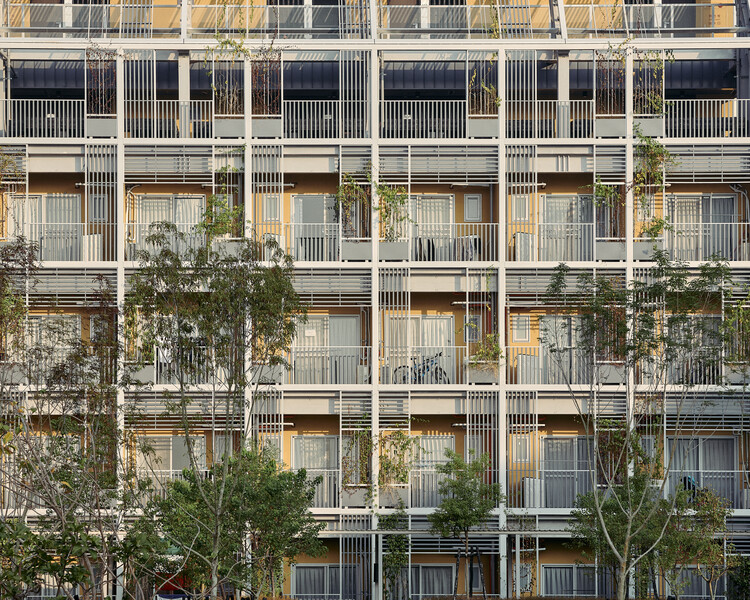


Also, the wooden planks from the old buildings were treated and reused as the wooden frame for the pivoted door at C-House. As to reduce the carbon emissions, we have opted for green materials like CLT (cross-laminated timber) and recycled LED glass insulation blocks for the façade and internal partition.
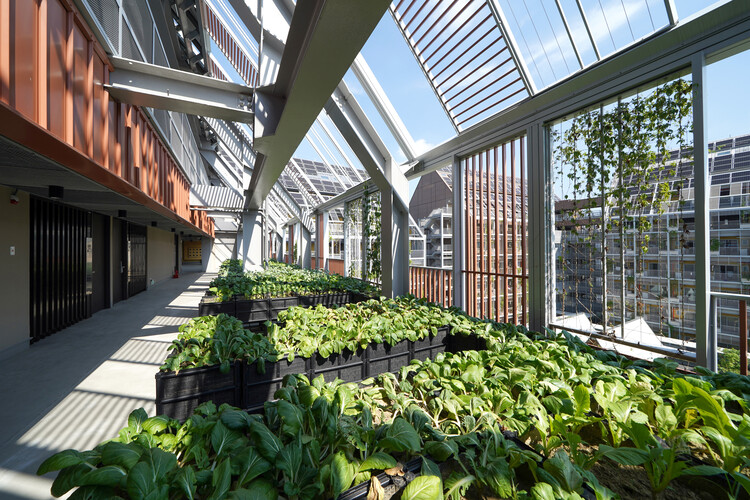

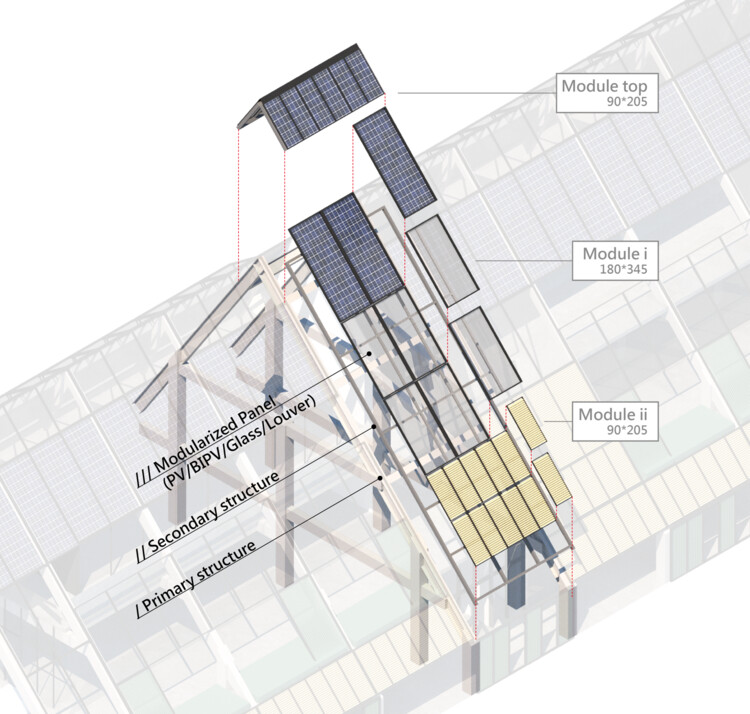
In order to design for disassembly, steel was chosen as the structural material rather than reinforced concrete. Modular building components such as prefabricated PC boards, metal louvers for the façade, prefabricated floor panels for slabs were used in conjunction with BIM software to comprise the BAMB database. In order to further fulfill the spirit of circular economy, the ownership for the elevator, lighting, furniture, and sanitary fixtures were replaced with usership—so in other words, rented instead of purchased.



































