
-
Architects: Richard Neutra
- Year: 1947
-
Photographs:Thom Watson, Flickr User: Caffinara
Text description provided by the architects. One of the most important architects of the 20th Century, yet often overlooked, Richard Neutra has been on the forefront of modern residential architecture. After moving to the United States from Vienna, Austria in 1923, Neutra worked with Frank Lloyd Wright and Rudolf Schindler until 1930 when he started his own practice.
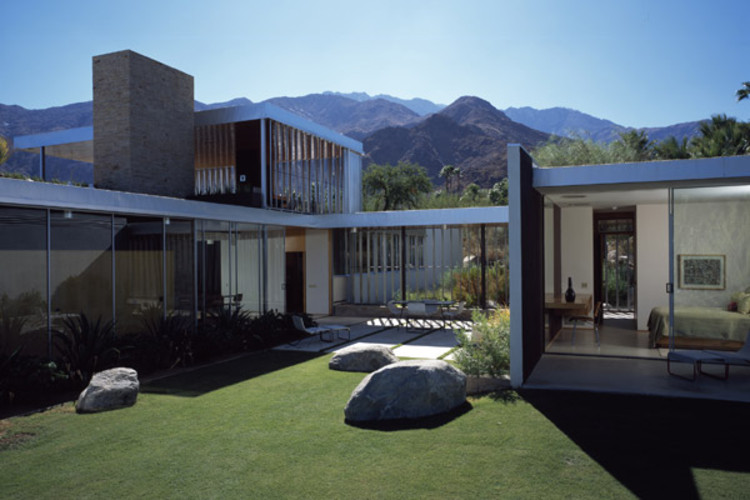

One of Neutra’s several iconic projects is the Kaufmann House in Palm Springs, California. Completed between 1946-1947, the Kaufmann House was a vacation home for Edgar J. Kaufmann Sr. and his family to escape the harsh winters of the northeast.

10 years after the design of Fallingwater by Frank Lloyd Wright in Bear Run, Pennsylvania, the Kaufmann’s were looking for a residence that could be used to escape the cold winters of the northeast, which would primarily be used during January.

After seeing Wright’s Taliesin West, Kaufmann was unimpressed and gave his commission to Richard Neutra. Unlike Taliesin West, which implemented more earthy tones and materials, Neutra employed a more modernist and international style approach using glass, steel, and some stone in the design.
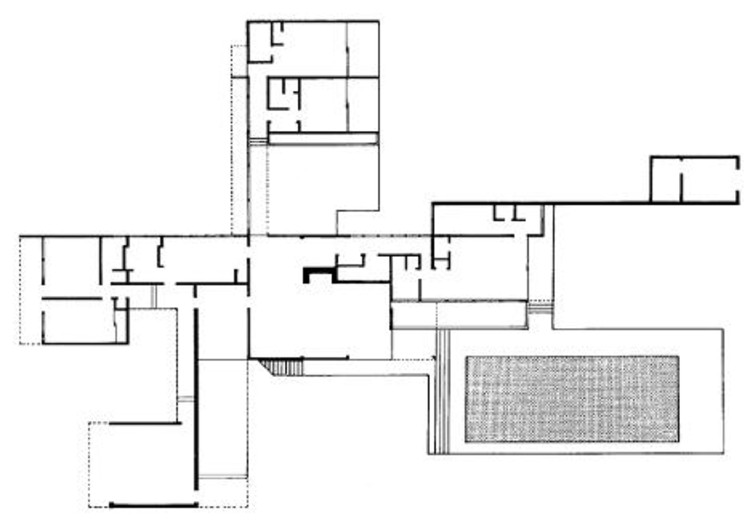
The design of the house is quite simplistic; at the center of the house is the living room and the dining room that is the heart of the house and the family activity. The rest of the house branches out like a pinwheel in each of the cardinal directions. From the center of the house each wing that branches out has its own specific function; however, the most important aspects of the house are oriented east/west while the supporting features are oriented north/south.

The north and south wings are the most public parts of the house that connect to the central living area. The south wing consists of a covered walkway that leads from the center of the house to the carport.

The north wing is the guest’s quarters that are publicly accessible, but retain their private needs as they are separated from the rest of the house. The west wing of the house is the service wing, which is fairly secluded from the rest of the open plan design. The east wing is the most privatized aspect of the house as it is the Kaufmann’s master suite.

The house’s swimming pool is one of the most iconic and recognizable aspects of the Kaufmann House; however, it is not solely a photographic gem or simply a recreational feature. The swimming pool creates a compositional balance of the overall design of the house. The house alone is unbalanced and heavy as the wings are not equally proportioned, but with the addition and placement of the swimming pool there is a cohesive balance and harmony throughout the design.

The low, horizontal planes that make up the pinwheel design bring the house closer to the landscape making it appear as if it is hovering above the ground.

The floating effect is emphasized through a series of sliding glass doors that open up to cover walkways or patios. The way in which Neutra designed the Kaufmann House was such that when the sliding glass doors were opened the differentiation of interior and exterior was blurred as if it was a sinuous space.

The flow from interior to exterior space is not simply a spatial condition rather it is an issue of materiality that creates the sinuous experience. The glass and steel make the house light, airy, and open, but it is the use of stone that solidifies the houses contextual relationship. The light colored, dry set stone, what Neutra calls “Utah buff,” brings out the qualities of the glass and steel, but it also blends into the earthy tones of the surrounding landscape of the stone, mountains, and trees.

The Kaufmann House has gone through several owners after the Kaufmann’s owned the house, which led to the house to fall in disrepair and a lack of concern and preservation of the modern dwelling. However, a couple that appreciated 20th Century modern homes restored the house back to its original luster with the help of Julius Shulman. The Kaufmann House is now considered to be an architectural landmark and one of the most important houses in the 20th Century.





















