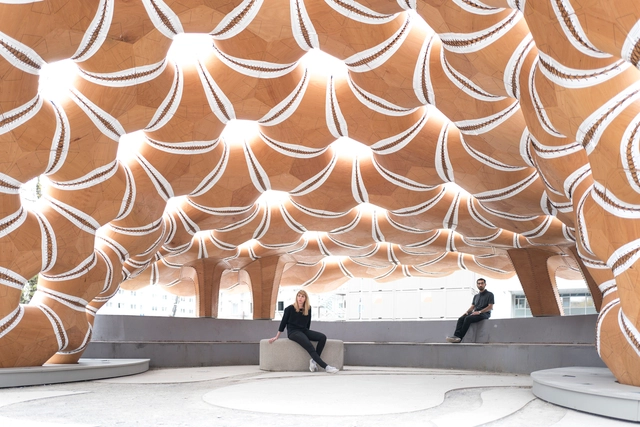
Andanzas y visiones españolas is the book in which Miguel de Unamuno collects his experiences during excursions through Spain's cities and countryside, accompanied by friends and colleagues. More than a precise geographical description, the text consists of narratives in which each region and every feature of the territory leaves a deep imprint on his thought. The literary discourse actively weaves the diversity of setting, climate, and contextualism as foundational threads, presenting the territory not only as a physical place but also as a space for reflection and contemplation. This attentive engagement with the landscape—so diverse within Spanish architecture—also resonates in the built environment, fostering in contemporary practice a sensitive adaptation to the country's varied climatic conditions, both through design strategies and material choices.