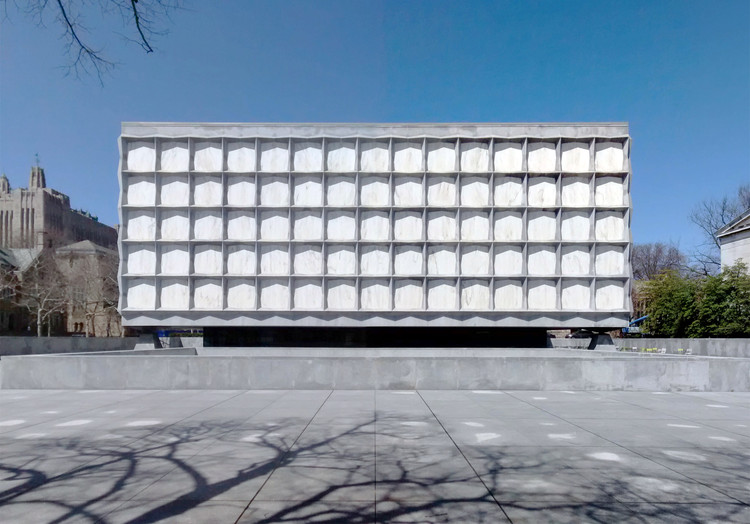
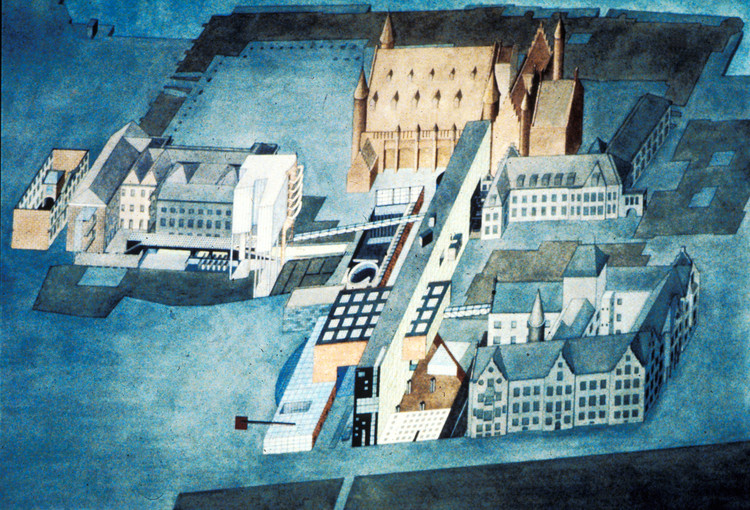
As the dust settled following the Second World War much of Europe was left with a crippling shortage of housing. In Milan, a series of plans were drafted in response to the crisis, laying out satellite communities for the northern Italian city which would each house between 50,000 to 130,000 people. Construction the first of these communities began in 1946, one year after the end of the conflict; ten years later in 1956, the adoption of Il Piano Regolatore Generale—a new master plan—set the stage for the development of the second, known as 'Gallaratese'. The site of the new community was split into parts 1 and 2, the latter of which was owned by the Monte Amiata Società Mineraria per Azioni. When the plan allowed for private development of Gallaratese 2 in late 1967, the commission for the project was given to Studio Ayde and, in particular, its partner Carlo Aymonino. Two months later Aymonino would invite Aldo Rossi to design a building for the complex and the two Italians set about realizing their respective visions for the ideal microcosmic community.[1]
























































_-_Administration_and_Cour_d'Honneur.jpg?1497053167)
_-_Midway_2.jpg?1497053349)
_-_USG_Building_and_Ho_O_den.jpg?1497053430)
_-_Birds_Eye.jpg?1497053224)
_-_Map.jpg?1497053293)
.jpg?1487999073)
.jpg?1487999184)
.jpg?1487999406)
.jpg?1487999574)
.jpg?1487999153)
.jpg?1503671953)


.jpg?1503672004)
.jpg?1503671990)
















